The pH of coffee typically ranges from 4.85 to 5.10. Learn what is the pH of coffee and how this mild acidity influences taste, aroma, and digestion.
Coffee lovers often wonder about its acidity. The pH level plays a big role in the taste and quality of your brew. It influences the flavor, aroma, and overall coffee experience. Coffee’s acidity can also affect your stomach if you are sensitive to acidic foods.
Understanding the pH of coffee helps you appreciate why some brews taste better to you than others. It also helps in making informed choices about what type of coffee to drink. So, what exactly determines the pH of your favorite cup? Let’s dive into the factors that influence the acidity in coffee and what it means for your daily cup of joy.
Credit: www.baybeans.com.au
What Is Ph?
Coffee is a beloved beverage enjoyed by millions every day. But have you ever wondered about its pH? Understanding the pH of coffee helps you know more about its taste, health effects, and brewing methods. In this section, we’ll dive into what pH is and why it matters.
Definition Of Ph
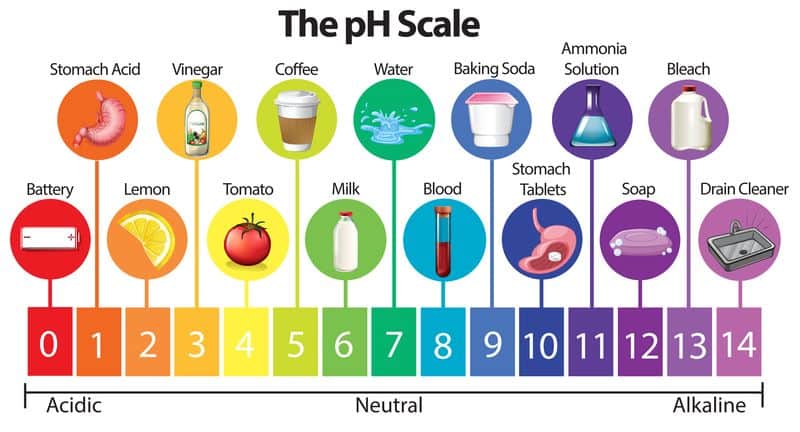
pH stands for “potential of hydrogen.” It measures how acidic or basic a substance is. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral. Below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is basic.
Here’s a simple table to illustrate:
| pH Value | Type |
|---|---|
| 0-6 | Acidic |
| 7 | Neutral |
| 8-14 | Basic |
For example, lemon juice has a pH around 2, making it very acidic. Water has a pH of 7, making it neutral. Baking soda has a pH around 9, making it basic.
The pH of coffee typically falls between 4.85 and 5.10, making it slightly acidic. This acidity impacts its flavor and how it interacts with your body.
Understanding the pH of coffee helps you choose beans and brewing methods that suit your taste and health preferences.
Importance Of Ph Scale
The pH scale is crucial for many reasons. It affects taste, health, and even the environment.
First, pH influences taste. Acidic foods and drinks, like coffee, have a sharp, tangy taste. Basic substances taste bitter. Knowing the pH helps you adjust recipes and brewing methods.
Second, pH impacts health. Highly acidic foods can cause stomach issues. Low-acid coffee can be gentler on your stomach. Knowing the pH helps you make healthier choices.
Third, pH affects the environment. Plants grow better in specific pH ranges. Water quality is judged by its pH. A balance is necessary for a healthy ecosystem.
Here are some key points:
- pH affects taste: Acidic = tangy, Basic = bitter
- pH impacts health: Acidic foods can cause stomach issues
- pH affects the environment: Plants and water quality depend on pH balance
Understanding pH helps you make informed choices about coffee and many other aspects of life.

Credit: www.solaicoffee.com
Coffee Composition
Coffee is a beloved beverage enjoyed by millions around the globe. But have you ever wondered what gives coffee its unique taste and varying pH levels? The answer lies in its composition. Understanding what coffee is made of can help us appreciate its flavors and how it affects our body. In this section, we will delve into the main ingredients of coffee and the acids that influence its pH.
Main Ingredients
Coffee is made up of a complex mixture of compounds. Each cup contains a blend of water, caffeine, oils, and other elements that contribute to its flavor and aroma. Here are the main ingredients found in coffee:
- Water: The primary component of coffee, making up about 98% of the beverage.
- Caffeine: A natural stimulant that provides the energizing effect coffee is known for.
- Oils: These are extracted from coffee beans during brewing and contribute to the flavor and mouthfeel.
- Proteins and Amino Acids: These are present in small amounts and can affect the taste and aroma.
- Carbohydrates: Mainly in the form of sugars, which add sweetness to the coffee.
- Minerals: Including potassium, magnesium, and calcium, which can influence the pH level.
Each of these ingredients plays a role in the overall profile of coffee. The balance of these components can vary depending on the type of coffee bean, the roasting process, and the brewing method. For instance, darker roasts generally have less acidity than lighter roasts.
Acids In Coffee
Acidity is a key characteristic of coffee, influencing both its flavor and pH level. Coffee contains a variety of acids, each contributing to its unique taste. Here are some of the main acids found in coffee:
| Acid | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Chlorogenic Acid | This is the most abundant acid in coffee. It contributes to the bitterness and is known for its antioxidant properties. |
| Quinic Acid | Forms when coffee is brewed for a long time. It adds to the sourness and can affect the perceived acidity. |
| Citric Acid | Gives coffee a bright, fruity flavor. More prevalent in lighter roasts. |
| Acetic Acid | Provides a vinegar-like taste. It can be more noticeable in over-extracted coffee. |
| Malic Acid | Similar to the acid found in apples. It imparts a tart, crisp flavor. |
The presence and concentration of these acids can vary. Factors like the origin of the coffee bean, the roast profile, and the brewing method all play a part. Light roasts tend to have higher acidity, while darker roasts are less acidic. Different brewing methods can also extract these acids in varying amounts, impacting the overall pH of the coffee.
Ph Of Coffee Types
Coffee is not just a morning beverage. It is a science. The pH level of coffee influences its taste, acidity, and overall experience. Different types of coffee have varying pH levels, which can affect your stomach and teeth. Let’s explore the pH of different coffee types: black coffee, espresso, and cold brew.
Black Coffee
Black coffee is a classic favorite. It is made by brewing roasted coffee beans with hot water. The pH of black coffee usually ranges from 4.85 to 5.10. This slightly acidic nature gives it a unique flavor profile. Here are some factors that can influence the pH of black coffee:
- Roast Level: Darker roasts tend to have a lower pH, making them more acidic.
- Brewing Time: Longer brewing times can extract more acids, reducing the pH.
- Water Quality: The pH of the water used can impact the final pH of the coffee.
Understanding the pH of black coffee can help you make better brewing choices. If you have a sensitive stomach, you might prefer a lighter roast with a higher pH.
Espresso
Espresso is a concentrated form of coffee. It is brewed by forcing hot water through finely-ground coffee beans. The pH of espresso typically falls between 4.5 and 5.0. This lower pH gives espresso its strong, bold flavor. Several factors can influence the pH of espresso:
- Grinding Size: Finer grinds can increase the extraction of acids, lowering the pH.
- Pressure: Higher pressure can extract more acids, affecting the pH.
- Bean Type: Arabica beans usually have a higher pH compared to Robusta beans.
Knowing the pH of espresso can help you tweak your brewing process. If you prefer a less acidic espresso, consider using coarser grinds and lighter roasts.
Cold Brew
Cold brew is made by steeping coffee grounds in cold water for an extended period. The pH of cold brew ranges from 5.0 to 5.2, making it less acidic than hot brewed coffee. This less acidic nature makes cold brew a smoother option. Factors affecting the pH of cold brew include:
- Steeping Time: Longer steeping times can extract more compounds, altering the pH.
- Temperature: Cold water extracts fewer acids, leading to a higher pH.
- Bean Type: Just like other coffee types, the bean variety affects the pH.
Cold brew’s higher pH makes it a great choice for those with sensitive stomachs. It is also versatile, as you can dilute it to your preference, further adjusting the pH.
Factors Influencing Ph
Coffee is a beloved beverage enjoyed by millions worldwide. One aspect that plays a significant role in its flavor profile is its pH level. Understanding the factors influencing the pH of coffee can help you better appreciate the complexities of your favorite brew. From the roasting process to the brewing method, various elements can affect the acidity and overall taste of your coffee.
Roasting Process
The roasting process is a crucial factor that influences the pH of coffee. During roasting, coffee beans undergo several chemical changes that impact their acidity. Here are some key points to consider:
- Light Roast: Lightly roasted beans generally have a higher acidity. The pH tends to be lower, making the coffee taste brighter and more tangy.
- Medium Roast: Medium roasts strike a balance between acidity and sweetness. The pH level is moderately acidic, offering a well-rounded flavor.
- Dark Roast: Dark roasted beans are less acidic. Their pH is higher, resulting in a smoother, more robust flavor.
Below is a table summarizing the impact of roasting levels on coffee pH:
| Roast Level | Acidity | pH |
|---|---|---|
| Light Roast | High | Lower (more acidic) |
| Medium Roast | Medium | Moderate |
| Dark Roast | Low | Higher (less acidic) |
During roasting, the breakdown of chlorogenic acids significantly affects the final acidity of the coffee. The longer and hotter the roasting process, the more these acids decompose, leading to less acidic coffee.
Brewing Method
The brewing method also plays a vital role in determining the pH of coffee. Different techniques can extract varying levels of acidity from the coffee grounds. Consider these points:
- Drip Coffee: This method typically results in a balanced acidity. The water temperature and brewing time are crucial factors.
- French Press: French press coffee tends to be less acidic. The longer steeping time allows more oils and compounds to mix, raising the pH.
- Espresso: Espresso is known for its high acidity. The quick extraction process concentrates the acidic compounds, lowering the pH.
- Cold Brew: Cold brew coffee is less acidic. The cold water extraction process yields a smoother, less tangy flavor.
Below is a table summarizing the impact of brewing methods on coffee pH:
| Brewing Method | Acidity | pH |
|---|---|---|
| Drip Coffee | Moderate | Moderate |
| French Press | Low | Higher (less acidic) |
| Espresso | High | Lower (more acidic) |
| Cold Brew | Low | Higher (less acidic) |
Water temperature, grind size, and brewing time are key factors in each method. Higher temperatures and finer grinds generally extract more acids, lowering the pH.
Measuring Ph
Coffee is a beloved beverage enjoyed by millions around the world. Its flavor, aroma, and even health benefits are influenced by its pH level. Understanding the pH of coffee can help you enhance its taste and ensure it suits your preference. Measuring the pH of coffee is essential for both casual coffee drinkers and enthusiasts.
Ph Strips Vs. Meters
There are two main methods to measure the pH of coffee: pH strips and pH meters. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages.
pH Strips:
- Cost-effective: pH strips are generally cheaper than pH meters.
- Easy to use: Simply dip the strip into the coffee and compare the color change to a pH scale.
- Portable: They are small and easy to carry around.
- Accuracy: pH strips can be less accurate, especially with darker liquids like coffee.
pH Meters:
- More accurate: pH meters provide a precise pH reading.
- Reusable: Unlike strips, meters can be used multiple times.
- Requires calibration: pH meters need to be calibrated regularly to maintain accuracy.
- Higher cost: pH meters are more expensive and may require batteries or electricity.
| Feature | pH Strips | pH Meters |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Low | High |
| Accuracy | Moderate | High |
| Ease of Use | Very Easy | Moderate |
| Portability | High | Moderate |
Diy Methods
If you do not have pH strips or a pH meter, there are some DIY methods to estimate the pH of coffee. These methods are less accurate but can give you a rough idea.
Baking Soda Test:
- Prepare a small cup of coffee.
- Add a pinch of baking soda to the coffee.
- If the coffee fizzes, it indicates that the coffee is acidic (pH less than 7).
Lemon Juice Test:
- Prepare a cup of coffee.
- Add a few drops of lemon juice to the coffee.
- If the coffee’s taste changes significantly, it suggests the coffee is near neutral or slightly acidic.
Red Cabbage Indicator:
- Boil red cabbage leaves in water to extract the purple juice.
- Mix a few drops of this juice with your coffee.
- If the color changes to red or pink, the coffee is acidic.
These DIY methods are simple and can be done with household items. They are not as precise as pH strips or meters but can be fun and educational.
Health Implications
Coffee is a beloved beverage worldwide, but its acidity can affect its health implications. The pH of coffee typically ranges between 4.85 and 5.10, making it slightly acidic. Understanding the health implications of coffee’s pH is important for making informed choices about your consumption.
Acidity And Stomach Health
The acidity in coffee can impact stomach health in several ways. For some people, the acidity can lead to stomach discomfort or exacerbate conditions like acid reflux. Here are a few points to consider:
- Heartburn and Acid Reflux: People with sensitive stomachs or GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease) may find that coffee’s acidity triggers symptoms.
- Stomach Ulcers: Those with stomach ulcers should be cautious, as the acidic nature of coffee can irritate the stomach lining.
- Digestive Issues: Some individuals may experience digestive issues, such as bloating or gas, due to the acidic content of coffee.
It’s important to note that not everyone will experience these issues. Each person’s tolerance to coffee’s acidity varies. If you find that coffee bothers your stomach, consider the following adjustments:
- Opt for low-acid coffee varieties.
- Avoid drinking coffee on an empty stomach.
- Try cold brew coffee, which is generally less acidic.
Impact On Taste
The pH of coffee significantly impacts its taste. Acidity in coffee is not necessarily a negative attribute; in fact, it can enhance the flavor profile. Here’s how:
- Bright and Lively Flavors: Acidity can give coffee a bright, tangy, and lively taste. This is often desired in lighter roasts.
- Fruit and Floral Notes: High acidity in coffee can bring out fruity and floral notes, adding complexity to the flavor.
Different brewing methods and types of coffee beans can affect the acidity and taste of your coffee. Here’s a comparison:
| Brewing Method | Acidity Level | Taste Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Espresso | High | Rich and Bold |
| Cold Brew | Low | Smooth and Mild |
| French Press | Medium | Full-bodied |
Understanding how acidity affects taste can help you choose the right coffee for your palate. If you prefer a less acidic cup, try dark roasts or low-acid coffee blends. For a brighter, more complex flavor, experiment with lighter roasts and different brewing methods.
Adjusting Ph Levels
Coffee’s pH level typically ranges from 4.85 to 5.10, making it slightly acidic. Some coffee lovers seek to adjust these levels for a smoother taste or to minimize digestive discomfort. Adjusting the pH can be achieved by adding certain ingredients or tweaking the brewing process. Below are some effective methods to modify your coffee’s pH level.
Adding Ingredients
One of the easiest ways to adjust the pH of coffee is by adding ingredients. These additions can either increase or decrease the acidity, making your coffee more pleasant to drink.
Baking soda is an alkaline substance that can neutralize the acidity in coffee. Adding a pinch can make a significant difference. Be careful not to use too much, as it can alter the taste.
- Milk: Adding milk or cream can lower the acidity. Dairy contains calcium, which neutralizes acid.
- Cinnamon: This spice can add a sweet flavor and reduce acidity. A small sprinkle can enhance both taste and pH balance.
- Eggshells: Surprisingly, adding crushed eggshells to coffee grounds can reduce acidity. Eggshells are alkaline and can help in neutralizing the acid during brewing.
Below is a simple table summarizing these ingredients and their effects on pH levels:
| Ingredient | Effect on pH |
|---|---|
| Baking Soda | Increases pH |
| Milk | Decreases Acidity |
| Cinnamon | Decreases Acidity |
| Eggshells | Increases pH |
Brewing Techniques
Adjusting the brewing technique can also impact the pH levels of your coffee. Here are some methods to consider:
Cold Brew: This method involves steeping coffee grounds in cold water for an extended period. Cold brewing produces coffee with lower acidity compared to hot brewing methods.
- Use coarsely ground coffee beans.
- Steep in cold water for 12-24 hours.
- Filter and serve over ice or dilute with water.
Water Quality: The quality of water used in brewing can affect pH levels. Using filtered or alkaline water can lead to less acidic coffee.
Brewing Time: The length of time coffee grounds are in contact with water can influence acidity. A shorter brewing time usually results in lower acidity.
- Espresso: Quick brewing time, less acidic.
- French Press: Longer brewing time, usually more acidic.
Grind Size: Finer coffee grounds can lead to higher acidity. Using a coarser grind can reduce acidity.
By experimenting with these techniques, you can find the perfect balance for your coffee’s pH levels.

Credit: www.jimsorganiccoffee.com
Taste Perception
When you drink coffee, you might notice its unique taste. This taste can be influenced by many factors, including its pH level. The pH of coffee usually ranges from 4.85 to 5.10, making it mildly acidic. Let’s dive into how this acidity affects the taste perception of coffee.
Acidity Vs. Bitterness
Acidity and bitterness are two key taste elements in coffee. They can greatly affect your overall enjoyment. Understanding the difference can help you pick the perfect cup.
Acidity in coffee is often described as a bright, tangy, or sharp taste. This is because of the organic acids present. Here are some common acids found in coffee:
- Citric Acid: Found in citrus fruits, it gives a lemony taste.
- Malic Acid: Found in apples, it provides a tart flavor.
- Phosphoric Acid: Found in sodas, it contributes to a sparkling sensation.
On the other hand, bitterness in coffee comes from compounds like caffeine and chlorogenic acids. These compounds can become more pronounced if the coffee is over-extracted or roasted too dark.
To understand the balance between acidity and bitterness, consider this table:
| Factor | Acidity | Bitterness |
|---|---|---|
| Light Roast | High | Low |
| Medium Roast | Moderate | Moderate |
| Dark Roast | Low | High |
Balancing acidity and bitterness can create a complex and enjoyable flavor profile. Experiment with different roasts to find your favorite balance.
Flavor Profiles
Coffee flavor profiles are diverse. They depend on the origin, roast level, and brewing method. Let’s explore how these factors contribute to the flavor.
Origin plays a significant role. Coffee beans from different regions have unique characteristics:
- Africa: Often fruity and floral.
- South America: Nutty and chocolaty.
- Asia: Earthy and spicy.
Roast level also influences flavor. Here’s a quick overview:
- Light Roast: Bright, acidic, and fruity.
- Medium Roast: Balanced, sweet, and complex.
- Dark Roast: Rich, bold, and bitter.
Finally, brewing method affects the flavor profile. Different methods extract flavors differently:
- Espresso: Intense and concentrated.
- Drip Coffee: Clean and balanced.
- French Press: Full-bodied and robust.
Each element, from origin to brewing, contributes to the final taste. Experiment with various combinations to discover your ideal cup. Enjoy the journey of tasting and exploring the world of coffee.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Coffee Acidic Or Alkaline?
Coffee is acidic. It typically has a pH between 4. 85 and 5. 10. This acidity can affect some people’s digestive systems.
What’s The Ph Of Black Coffee?
The pH of black coffee typically ranges from 4. 5 to 6. It depends on the coffee beans and brewing method.
Is Coffee Acidic To The Stomach?
Yes, coffee is acidic to the stomach. It can cause irritation and discomfort for some people. Drinking coffee on an empty stomach may increase acidity.
What Is The Ph Of Coca Cola?
The pH of Coca Cola is approximately 2. 5. This acidic level is due to the presence of phosphoric acid.
Conclusion
Understanding the pH of coffee helps you enjoy your cup better. Coffee’s acidity varies, impacting its taste and your health. Choosing the right coffee can make your mornings brighter. Remember, balance is key. Experiment with different beans and brewing methods.
Find what suits your taste buds. Enjoy your coffee journey!








